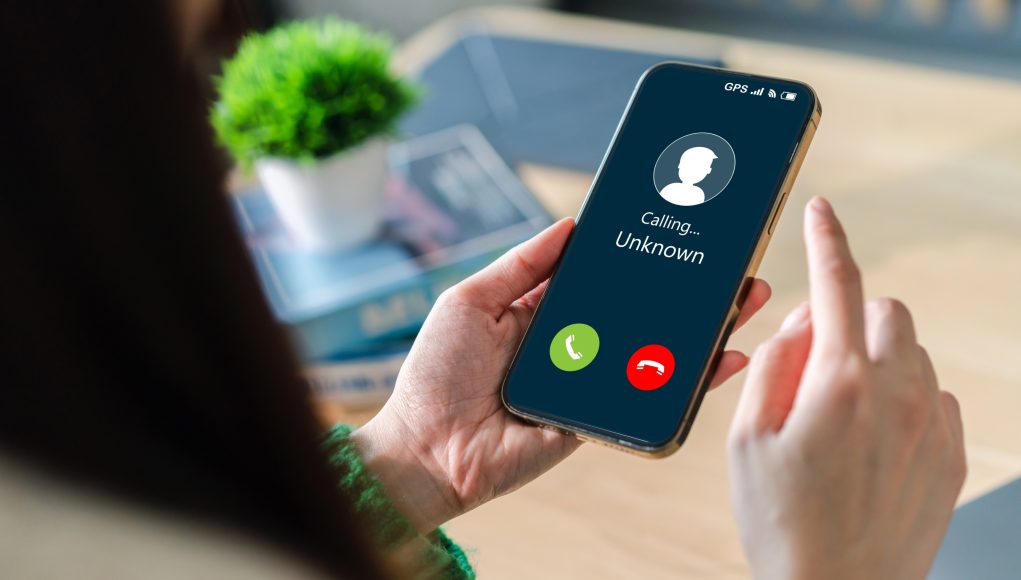
(Singapore, 11.02.2026)Today, the Philippine Threat Landscape Report 2025 by Check Point Software Technologies, released that a 423% surge in phishing websites and warning that cybercriminals are shifting toward large-scale, industrialized fraud operations targeting the country’s mobile-first population.
The findings were first unveiled during the inaugural CXO Elite Club Philippines dinner, a private gathering of senior executives and industry decision-makers.
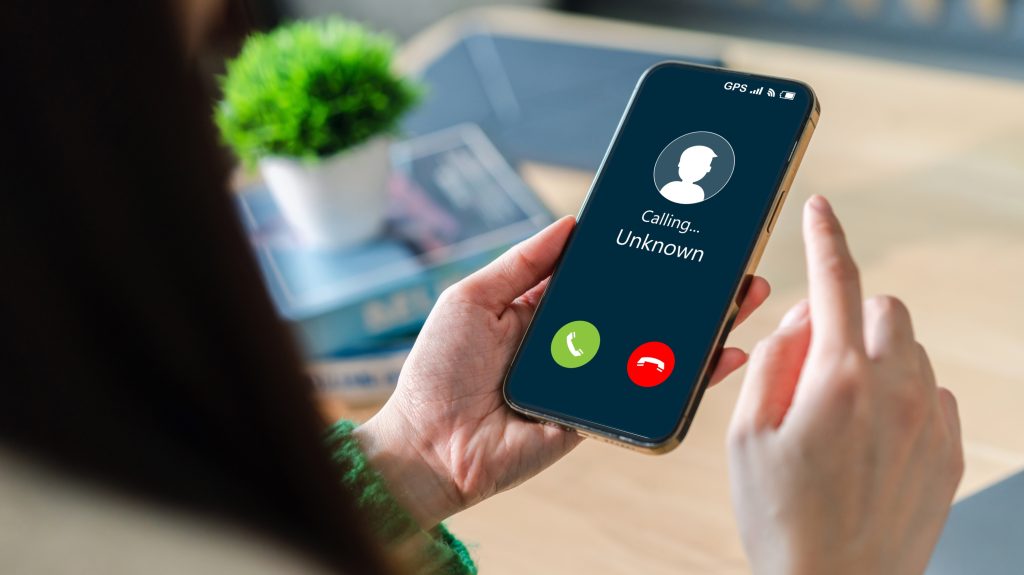

According to the report, phishing websites increased dramatically from 731 in 2024 to 3,824 in 2025. SMS-based phishing, or “smishing,” has emerged as the dominant threat vector, with attackers using telecom-level manipulation techniques to bypass mobile trust barriers and scale fraud campaigns.
The research indicates that cybercriminals are moving beyond isolated technical intrusions toward systemic operations driven by automation and deception. Rapid cloud adoption and heavy reliance on third-party vendors are also expanding the national attack surface faster than many organizations can secure it.
Ransomware incidents nearly doubled, rising from nine recorded attacks in 2024 to 17 in 2025. The Qilin ransomware group was identified as the most aggressive actor, deploying cross-platform ransomware and double extortion tactics across sectors including finance, retail, healthcare, manufacturing, food services, media, real estate and business services.
Meanwhile, social media impersonation cases increased 37%, from 940 to 1,291 incidents. Financial institutions have been particularly affected, as attackers leverage AI-powered chatbots and executive impersonation to promote fraudulent investment schemes and harvest credentials.
The report also highlights accelerating data exposure risks. Source code leaks more than doubled year-on-year, from 38 to 81 cases. Third-party breach incidents rose from eight to 29, underscoring the Philippines’ growing vulnerability to supply-chain attacks.
Researchers warn that underground SIM card markets and celebrity deepfakes are fueling sophisticated fraud ecosystems that now operate as cross-border networks rather than isolated scams.
The report outlines several sectors facing elevated risk:
- Government and Public Sector: Subject to high-visibility DDoS attacks and website defacements linked to political events and hacktivism.
- Financial Services: Facing large-scale fraud exposure through account takeovers, brand impersonation and credential harvesting.
- Critical Infrastructure: Targeted by reconnaissance and disruption attempts, particularly during geopolitical tensions.
- Education Platforms: Frequently exploited as testing grounds for emerging threat actors due to lower cyber maturity.
Looking ahead, Check Point predicts that artificial intelligence will amplify — rather than replace — existing fraud techniques in 2026, making scams faster, more convincing and more scalable. NFC payment fraud is expected to rise alongside increased adoption of Google Pay and local e-wallets. Supply-chain breaches are also projected to escalate as more Philippine organizations integrate AI tools and cloud services into daily operations.
Deepfakes and misinformation campaigns are anticipated to increasingly target brands, executives and political institutions.
“Cyberattacks in the Philippines are no longer defined by technical sophistication, but by scale, automation, and deception,” said Ritchelle Santos, Senior Cyber Threat Intelligence Analyst at Check Point Exposure Management Research. “In an environment where identity, trust and mobile channels are the new battleground, the safest organizations will be those that protect their digital footprints as carefully as they protect their networks.”
The report concludes that the Philippine threat landscape has shifted toward high-impact, high-visibility and low-complexity attack vectors, including phishing, identity abuse, cloud misconfigurations and external exposure risks. Addressing these systemic vulnerabilities will require a fundamental shift in national cyber defense strategies to safeguard the country’s rapidly expanding digital economy.